Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
What’s Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1?
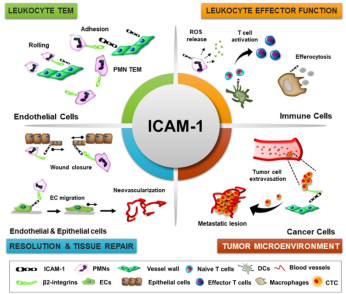
ICAM-1 (also known as Intercellular adhesion molecule-1) is a protein encoded by the human ICAM1 gene. ICAM-1 is a glycoprotein on the cell surface and belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is mainly expressed on endothelial cells, immune cells, and other cell types.
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 Main Functions
ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule-1) plays an important role in immune and inflammatory processes. The following are some of the main functions of ICAM-1:
Immune cell adhesion and migration
ICAM-1 is located on the cell surface and participates in the adhesion and migration of immune cells (such as white blood cells). When damaged tissue or infection occurs, ICAM-1 can interact with corresponding receptors (such as leukocyte integrin), promoting leukocyte proximity and adhesion to the damaged area, thereby achieving targeted migration of immune cells.
Inflammatory response regulation
During the inflammatory process, ICAM-1 participates in adhesion and regulation of inflammatory response by binding to leukocyte integrins. It can help regulate the release of inflammatory mediators, activation and chemotaxis of white blood cells, thereby affecting the degree and duration of inflammation.
Intercellular interactions
ICAM-1 acts as a bridge between cells, promoting cell adhesion and interactions. It participates in signal transmission between cells, regulates cell adhesion, migration, and morphology to maintain tissue structure and function.
Interactions with pathogens
ICAM-1 is also involved in the development of infectious diseases, especially with pathogens (such as viruses, bacteria, etc.). Some pathogens can use ICAM-1 to enter cells or tissues, leading to infection. Studying the interaction between ICAM-1 and pathogens is helpful to understand the infection process, and may provide clues for developing strategies to prevent and treat infectious diseases.
In summary, ICAM-1 plays an important role in immune and inflammatory processes, participating in cell adhesion and migration, regulating inflammatory responses, and intercellular interactions. The study of ICAM-1 function contributes to a deeper understanding of the pathogenesis of related diseases and is expected to provide new ideas for the development of treatment and intervention strategies.