What is Resistin?
What Is Resistin
Introduction
Resistin, originally described as an adipocyte-specific hormone, has been suggested to be an important link between obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes. Although its expression was initially defined in adipocytes, significant levels of resistin expression in humans are mainly found in mononuclear leukocytes, macrophages, spleen and bone marrow cells. Increasing evidence indicates that resistin plays important regulatory roles apart from its role in insulin resistance and diabetes in a variety of biological processes: atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (CVD), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, autoimmune disease, malignancy, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease and chronic kidney disease. As CVD accounts for a significant amount of morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes and without diabetes, it is important to understand the role that adipokines such as resistin play in the cardiovascular system. Evidence suggests that resistin is involved in pathological processes leading to CVD including inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, thrombosis, angiogenesis and smooth muscle cell dysfunction. The modes of action and signalling pathways whereby resistin interacts with its target cells are beginning to be understood.
How Does Resistin Work?
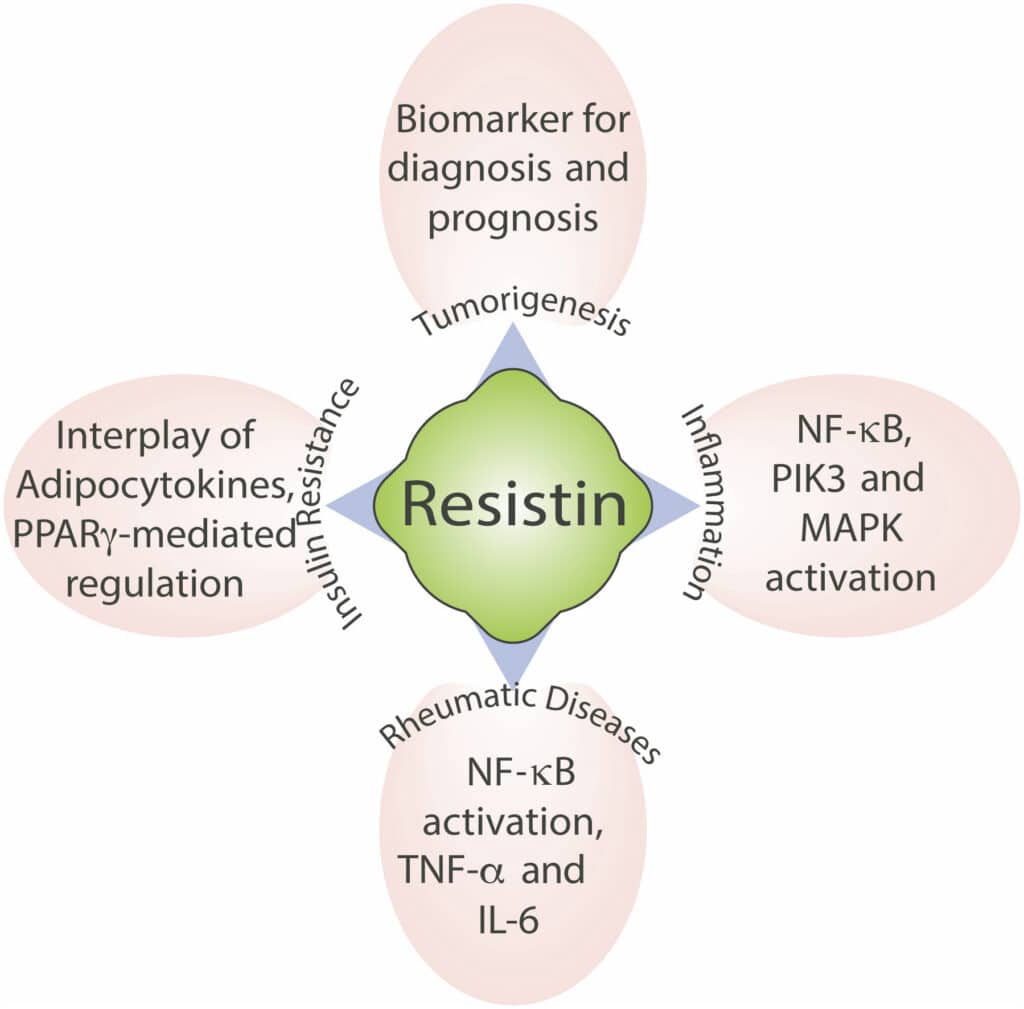
Resistin is a cysteine-rich hormone secreted from white adipocytes. Resistin is involved in insulin resistance and links obesity to diabetes in mice; it is involved in inflammation in humans. Resistin is exclusively expressed in white adipose tissue in rodents.
How Does Resistin&Leptin Work?
The adipokines, resistin and leptin are produced in fat tissue and each can act in the brain to affect metabolic functions, like food intake, insulin sensitivity and release and energy homeostasis. They also influence cardiovascular regulation.
Does Resistin Cause Diabetes?
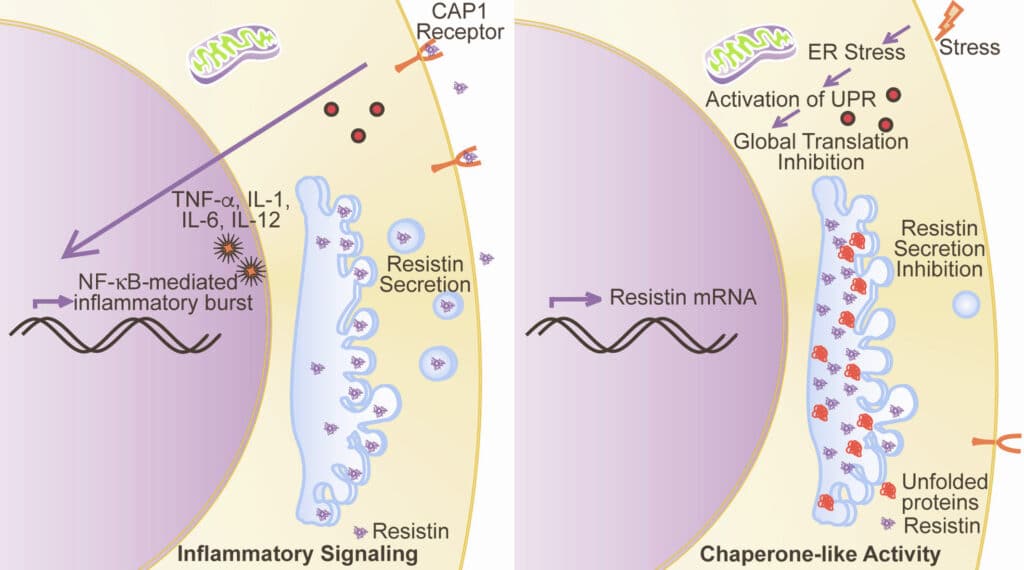
A new hormone has been identified that links obesity to type 2 diabetes. It has been called resistin (for ‘resistance to insulin’), and, although first identified in mice, it has also now been found in humans.
Does Resistin Cause Obesity?
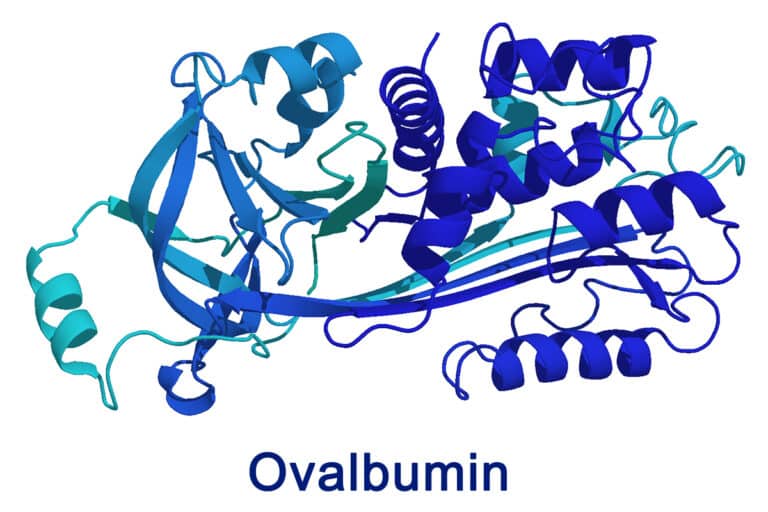
Ovalbumin: The primary protein in egg white, ovalbumin provides nourishment and binds digestive enzymes. It makes up approximately 54% of the protein in egg albumen .OVA inhalation produces allergic airway inflammation.
Why Is Resistin Released?
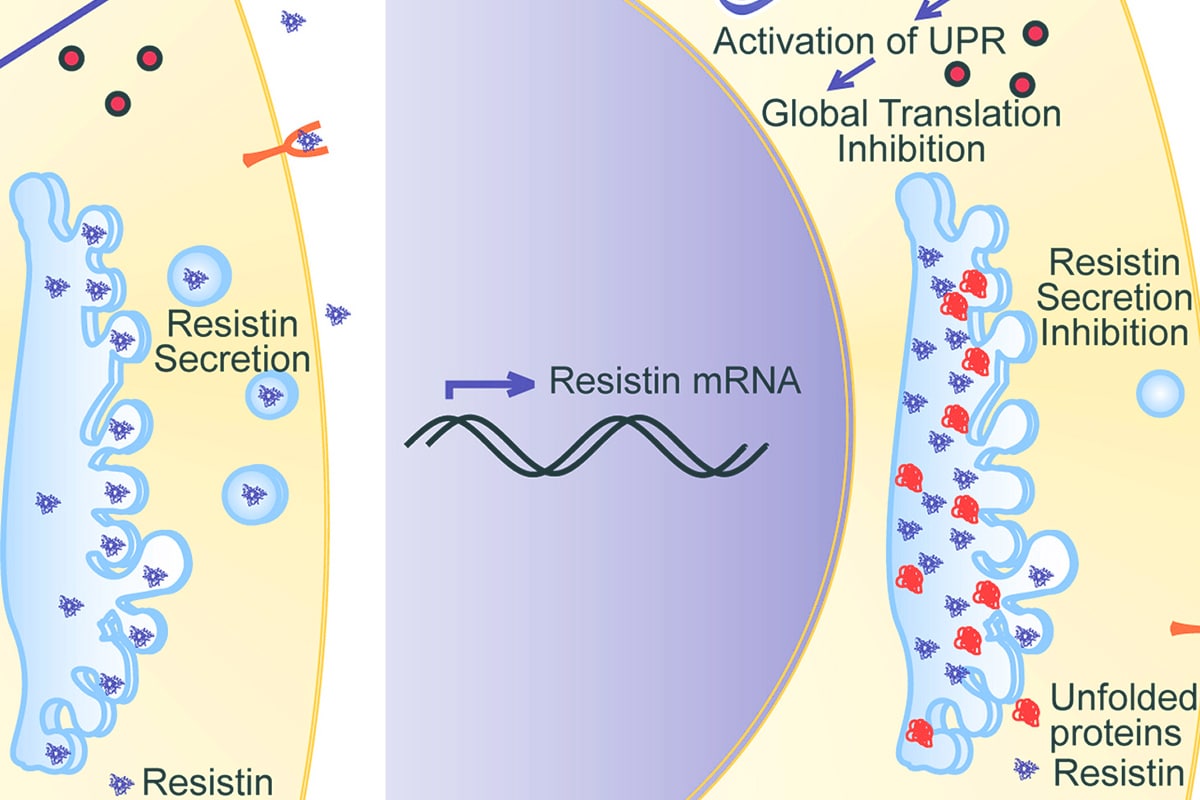
It is considered a pro-inflammatory molecule, which also plays an important role in the pathogenesis of diabetes and its complications. The release of resistin is often stimulated by the inflammatory process, IL-6, hyperglycemia and hormones such as growth hormone and gonadal hormones.