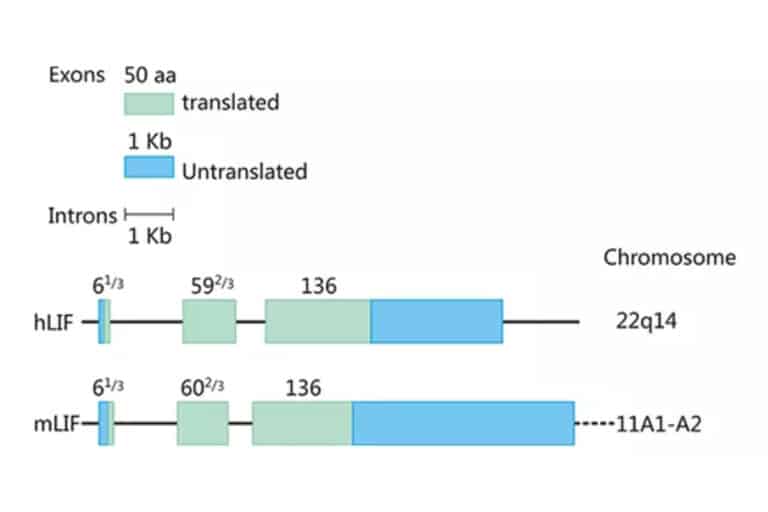
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor introduction Leukemia inhibitory factor, or LIF, is an interleukin 6 class cytokine that affects cell growth by inhibiting differentiation. When LIF levels drop, the cells differentiate. LIF derives its name from its ability to induce the terminal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells,thus preventing their continued growth. Other properties attributed to the cytokine…